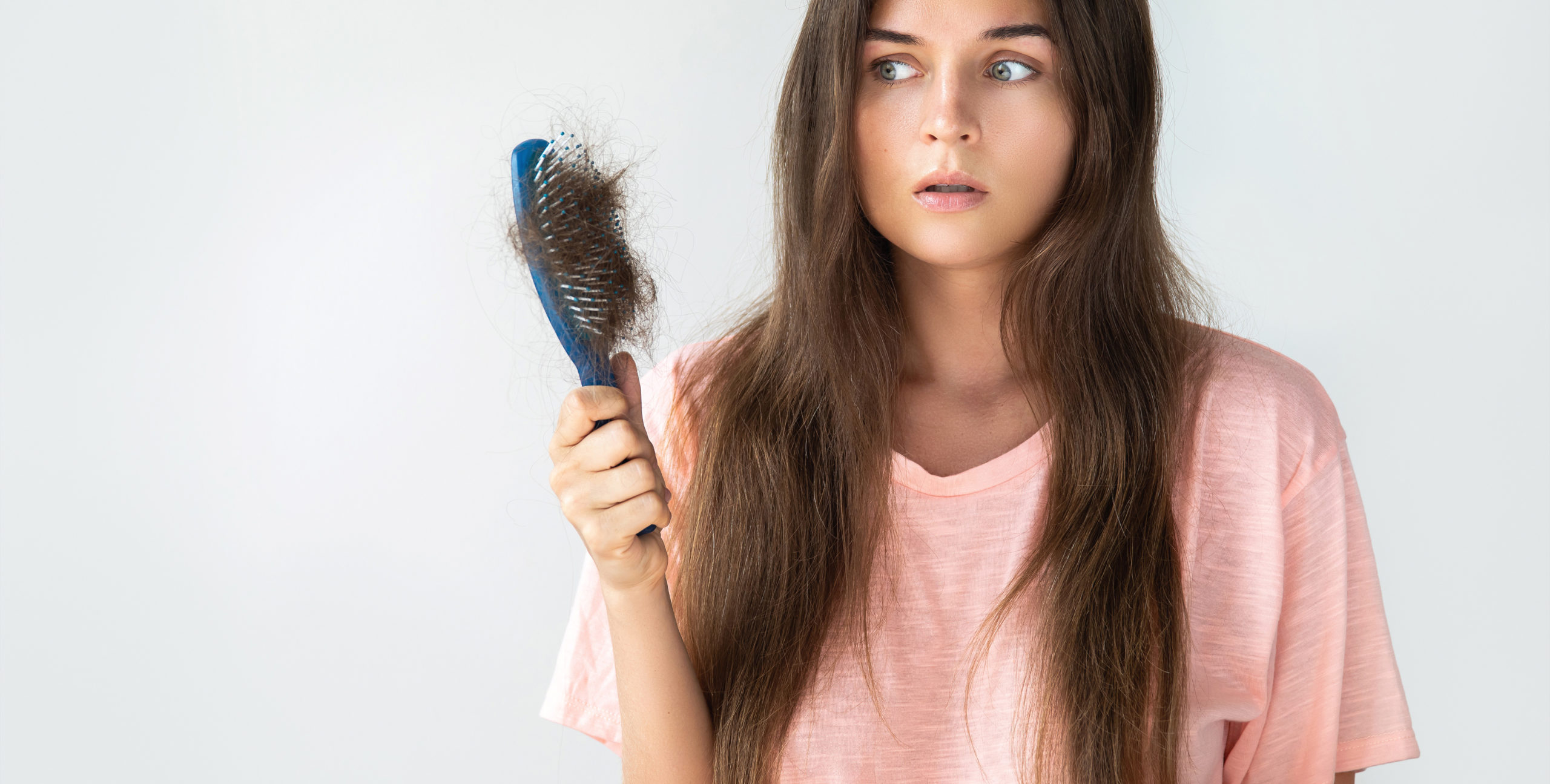
If you’re noticing hair coming out in your hands or clogging up your drain, it’s normal to be concerned. But you’re not alone; millions of Americans experience hair loss every year.
The natural question to ask is, why? Well, although there are several reasons for hair loss, it may be caused by thyroid disease.
Learning about the link between thyroid disease and hair loss could be the first step to replenishing a receding hairline or thinning locks.
Read on for a quick guide to thyroid disease and hair loss.
What Is Thyroid Disease?
The thyroid gland is found in your throat and makes hormones that are vital for your body to function correctly. When your thyroid produces too little hormone, this is called hypothyroidism. When it creates too much, it’s called hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid disease encompasses any conditions where the thyroid isn’t producing the correct amount of hormone, whether too active, or too inactive. Anyone can develop thyroid disease, but you’re at higher risk if you have a family history, other medical conditions, and during later life.
What Are the Symptoms of Thyroid Disease?
Depending on what type of hormone production you have, symptoms can vary. Underactive thyroid disease symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, memory problems, hair loss, and feeling cold.
Overactive thyroid disease symptoms include anxiety, weight loss, sleep problems, muscle weakness, hair loss, and feeling hot.
What you’ll notice is that both under- and overactive thyroid disease can cause hair loss.
How Does Thyroid Disease Cause Hair Loss?
There are different types of hair loss, from Alopecia areata (rapid, excessive hair loss) to telogen effluvium (hair thinning). The important thing to know is that hair has a lifecycle, and each strand isn’t growing at all times.
When you have thyroid disease, the lack or excess of hormones can trigger the scalp into a resting phase. This means that new hairs aren’t formed to balance natural hair loss, resulting in a noticeably thinner head of hair.
Thyroid disease-related hair loss usually occurs after prolonged hyper- or hypothyroidism.
What Is The Treatment for Thyroid Disease-Related Hair Loss?
If you’re noticing the signs of hair loss, the first thing to do is see your healthcare provider, and they’ll test you for thyroid disease. Often medications will resolve your hair loss, but this takes time.
While you’re waiting for regrowth, you should treat your scalp gently to encourage re-growth. Avoid bleaching, heat treatments, and use a specialist shampoo.
However, if you’re looking for an instant fix, the most effective option is plasma-rich platelet (PRP) treatment. This includes taking blood from the arm and injecting the plasma around the hair follicles. This contains a growth factor that will instantly trigger hair follicle regrowth.
Treat Thyroid Disease and Hair Loss Today
That’s a quick guide to the link between thyroid disease and hair loss. If you’re experiencing hair loss symptoms, it’s time to act now.
Visit a doctor, look after your scalp, and you should be able to reverse your hair loss. However, hair doesn’t grow overnight, so patience is vital.
If you’re looking for a quick fix, why not contact us today for a free consultation on PRP treatment?